
The NQR90-L-6000L double-cabin mobile refueling truck is based on a transport vehicle and is equipped with a refueling machine, control system, AI video imaging, automatic hose reel, refueling nozzle, and more. Mainly used for transporting and storing various petroleum derivatives, including gasoline, diesel, crude oil, lubricants, coal tar and other oil-based materials. Depending on its intended use and environmental requirements, it has multiple functions including oil suction, pumping and multiple tank loading and unloading capabilities. These versatile mobile fuel trucks effectively serve as mobile refueling stations.
The mobile refueling truck is equipped with an on-board computer tax-controlled refueling machine, which can pump the oil from the tanker truck into the refueling machine. The machine can measure refueling volume in liters or calculate the cost of refueling based on an entered monetary value. Flow meters can also be installed for precise measurement. These vehicles are highly adaptable and can be used in cities, suburbs, mines, ports, airports, train stations, rural roads and other places where conventional gas stations are not easily accessible. They provide a convenient solution for refueling all types of vehicles and equipment including cars, loaders, excavators, cranes, mining equipment and vessels. Mobile fuel trucks significantly improve the accessibility of fueling services, provide unparalleled flexibility and serve as mobile refueling stations to meet a wide range of needs.
product parameters: | |||
Product Name | Mobile Refueling Truck | Product Model | NQR90-L-6000L |
Gross Weight | Unknown | Tank Capacity | 6000L |
Rated Load Capacity | Unknown | Vehicle Compartment Size | 5675X2120X1600 |
Passenger Capacity | 1 | Driver Seating Capacity | 2 |
Number of Tank Compartments | 2 | Fueling Standard | API |
Explosion-proof Rating | VI | Configuration Dimensions | 4inch |
Winch Length | 10m | Fueling Nozzle | 1-inch fast flow rate |
Liquid Level System | Digital Display | Alarm System | Photoelectric Sensing |
Voltage | 24V | Power Source | Electric/Transmission |
Assembly Diagram
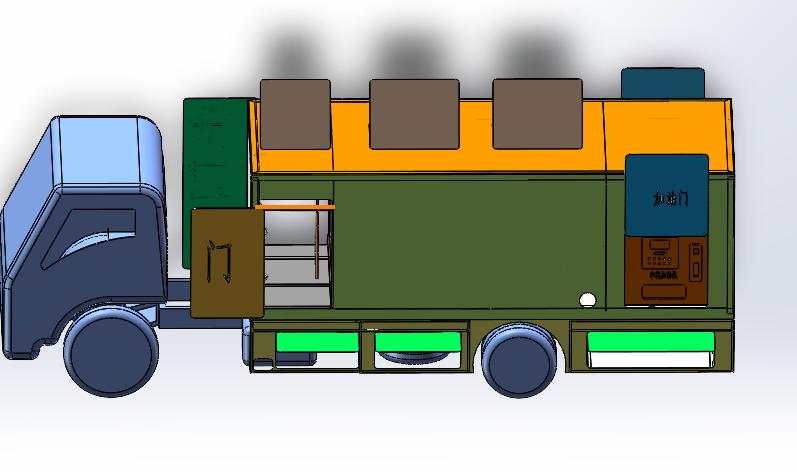
It adopts an all-aluminum alloy body, and the total mass complies with vehicle standards. The layout adopts a rear fuel refueling operation room. The front compartment is where the tool compartment and fire extinguishing system are located. There is a manhole inspection ladder for the upper body. The whole vehicle is equipped with three types: B, C, and D. Fire extinguishers and hatch doors are designed to be opened without obstacles.
The loading system is a full range of products suitable for API standards, including electrostatic equipment
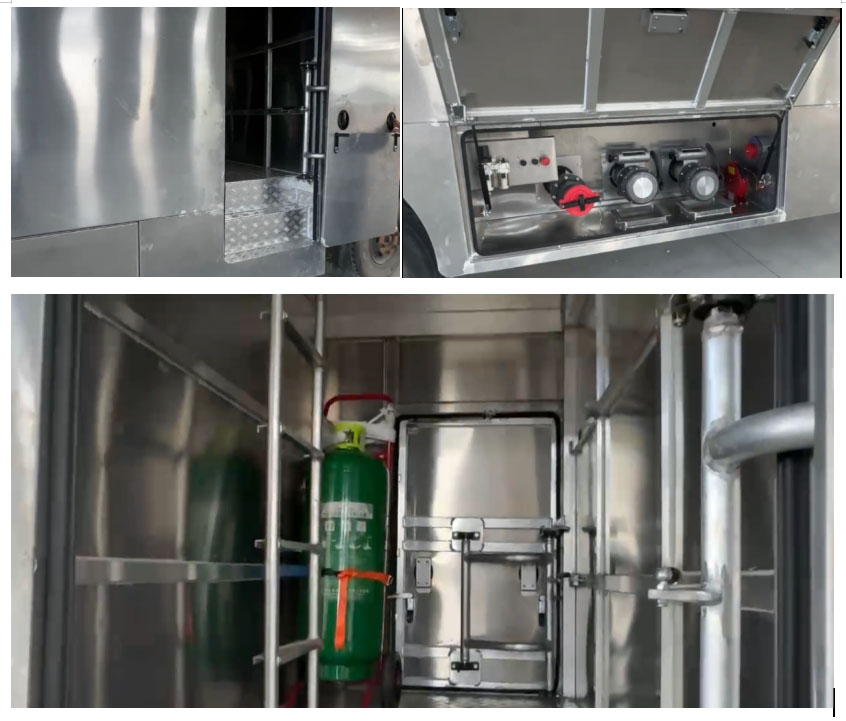
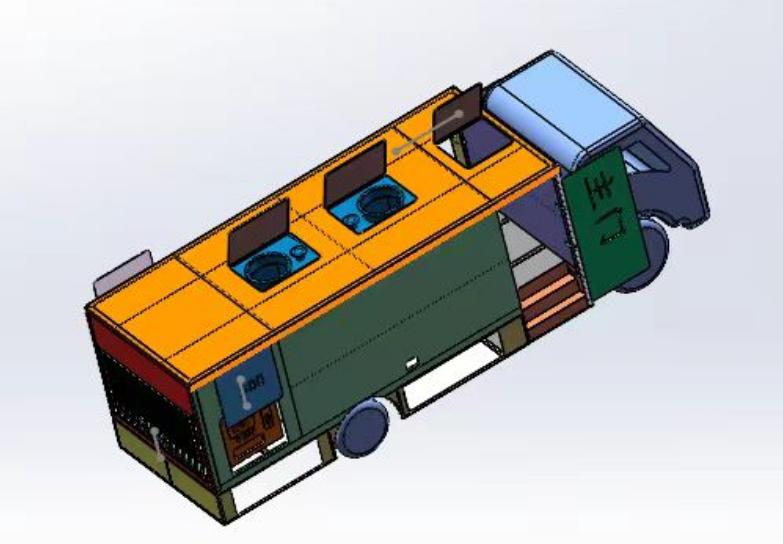

Introduction to electronic/electrical equipment
The front/rear lighting is used respectively, and the width lights are controlled by the on-board circuit. The fuel refueling device and equipment are turned off and put into sleep state, providing safety guarantee for driving.
It is also equipped with a backup battery pack 300, which can be selected according to customer conditions.

The control system consists of high liquid level, low level alarm system, visual system, printing system, refueling printing system, voltage protection system, explosion-proof system, AI video, etc., which can realize printing at any time, data accumulation throughout the day, video recording and storage and other information retention and query
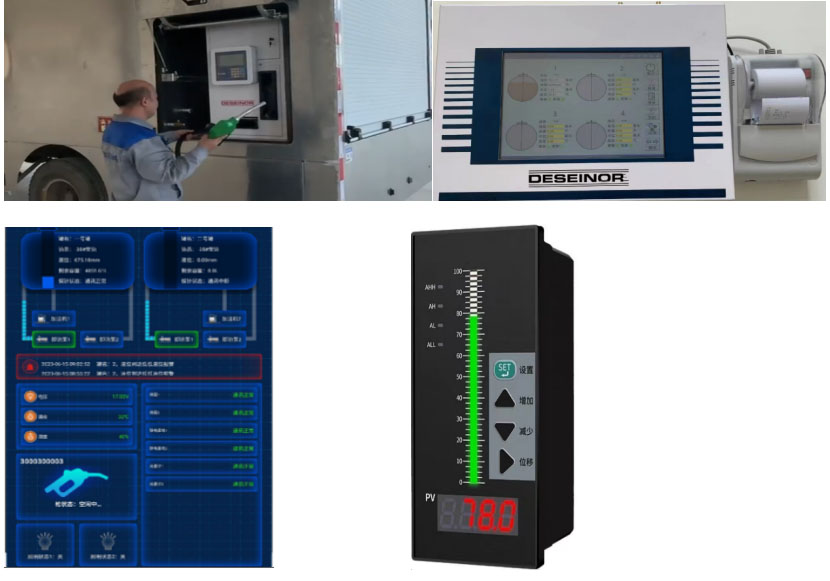

video effects

Safety Operating Instructions
User Operation
To ensure the cleanliness of the fuel tank truck, the tank and the oil transfer system should be cleaned regularly. The inner and outer joints of the oil transfer hose at both ends should be lubricated frequently to make the assembly and disassembly of the fuel tank truck easy. After each operation, the hoses should be cleaned promptly to ensure their cleanliness.
The use and maintenance of the fuel pump on the fuel tank truck should strictly follow the instructions provided in the user manual.
Before refueling, an anti-static rod should be inserted into damp soil, and the fuel tank truck's grounding strip should be properly connected. Good static electricity dissipation should be maintained throughout the operation.
The safety valve and filter mesh of the fuel tank truck should be regularly inspected and cleaned.
The tank and pipeline system should be cleaned periodically. The fuel tank truck should periodically check the connections at various points in the pipeline system for proper connection and reliable sealing.
The fuel tank truck should be equipped with an anti-static strip in accordance with the regulations. When static electricity encounters a high concentration of flammable gas residue inside the vehicle, an explosion may occur. The anti-static strip can effectively dissipate static electricity in areas where friction with the vehicle body and other parts frequently generates static electricity, ensuring safety. Installation method: It can be installed on a metal part of the chassis. After a period of use, when the lower part of the strip wears down, you can lower the upper rubber strip. If possible, users can install an anti-static grounding alarm device under the high-voltage wire of the fuel tank truck to prevent refueling inside the tank. It is strictly prohibited to use the hanging fire method frequently. Sometimes, the spark plug in the vehicle may accumulate carbon. When carbon buildup is severe in a cylinder, that cylinder cannot operate normally. To allow the cylinder to operate properly, the "hanging fire" method is used, leaving a gap of 3-4 millimeters between the spark plug and the high-voltage wire outside the cylinder. This method increases the energy for spark plug electrode sparking, enabling the cylinder to resume normal operation. However, the "hanging fire" method can easily lead to misfires if not done carefully. If gasoline drips onto the cylinder head, it can easily cause a fire. Therefore, it is only a temporary remedial measure. Proper maintenance should include regular cleaning and maintenance of the spark plugs, and the use of the "hanging fire" method should be avoided whenever possible.
Preparations Before Using the Fuel Tank Truck
Insert the grounding rod into the ground to ensure that it is "grounded." If the ground is dry, you can wet it to ensure good grounding. Check the grounding chain to ensure contact with the ground.
Open the control box door of the fuel truck and check the handles of all valves, ensuring they are in the closed position (vertical).
For the initial use of the oil pump without priming, you should add oil in advance. You can add about 10 liters of oil through the oil inlet.
Check the oil level in the gearbox, using the lower edge of the oil level gauge hole as the reference point. Add gear oil if the level is insufficient.
Check the position of the gear lever in neutral, the position of the power take-off lever in the horizontal-right position, and the position of the throttle controller at the minimum. Maintenance of the fuel tank truck includes various aspects, not just changing engine oil, as some may think. It's a comprehensive concept that involves changing and cleaning oil and filters for various engine systems (engine oil, gear oil, brake fluid, transmission oil, power steering fluid, windshield washer fluid, battery water, engine air filter, cabin air filter, fuel filter, air conditioning filter, etc.). It also includes the replacement and maintenance of vulnerable parts in the fuel truck, such as belts, batteries, brake pads, ball joints, clutch plates, shock absorbers, etc. There's also the aspect of making the fuel truck look good (washing, exterior paint care, interior trim care, etc.). Proper maintenance of the fuel tank truck helps maintain its performance and extend its service life. This discussion focuses on the maintenance of vulnerable parts in the fuel truck, including how to inspect, replace, and maintain them, as well as what issues might be indicated by the appearance of certain symptoms during maintenance.
Issues drivers should pay attention to while driving a fuel tank truck:
1、Check the operation of all gauges while the fuel tank truck is in motion.
2、Ensure the proper functioning of the steering system while driving.
3、Verify that the hand and foot brakes are functioning normally while on the road.
The purpose of the fuel tank truck vapor recovery system
During the loading and unloading process of the fuel tank truck, it achieves fully enclosed gas recovery, restricting the emission of vapors into the atmosphere. While unloading fuel through the discharge pipe, the vapors from the gas station's fuel tanks are recovered through the vapor return pipe back into the fuel tank truck. The fuel tank truck then takes these vapors back to the depot for processing, thereby achieving vapor recovery. Subsea valves, also known as emergency shut-off valves, are installed at the bottom of the tank and can replace traditional top-loading for bottom-loading, making operations more convenient, time-saving, and environmentally friendly. These valves have a cut-off groove on the valve body. In case of an accident involving the fuel tank truck, the cut-off groove breaks without affecting the tank's sealing, effectively preventing fuel leakage and ensuring the tank's safety. The breathing valve, when tilted at 70 degrees, seals effectively to prevent liquid spillage. The quantity hole is used to install a dipstick or liquid level gauge and is located on the manhole cover. Safety valves are specially designed for tanks, chemical tanks, and similar container products. They are set to open at different pressures based on user requirements to meet different needs. The main body is made of stainless steel for corrosion resistance, high sealing performance, and suitability for various environments. The spill prevention sensor is widely used in various container tanks when filling with liquid in a sealed manner. It serves as a safety device to prevent liquid overflow and provide advance warning. It is installed on the top manhole cover of the container tank. When the liquid level reaches the warning limit, the sensor will automatically sound an alarm and cut off the circuit.
Safety Operations for Fuel Tank Trucks:
1、Fuel tank trucks should be equipped with dedicated fire extinguishers and should have grounding chains and anti-static rods. While driving, the grounding chain should be in contact with the ground. During refueling or unloading, the anti-static rod must be inserted into damp soil.
2、The fuel tank filler hole should be tightly sealed, the drain valve and drain pipe should not leak, the tank vent should be unobstructed, the fuel pump inlet filter screen should be cleaned regularly, and after using the fuel delivery hose, the end caps should be immediately placed on both ends to prevent dirt from entering.
3、The carburetor and exhaust pipe of the internal combustion engine must not have backfires. The exhaust pipe should be installed in the front of the vehicle.
4、Personnel working with the fuel tank truck should not wear shoes with iron nails. Smoking near the fuel tank is strictly prohibited, and open flames are not allowed.
5、When parked, stay away from open flames, and in hot seasons, choose a shaded parking spot. During thunderstorms, do not park under tall trees or power lines. If the vehicle stops midway during a journey, there should be someone on guard.
6、During maintenance, if an operator needs to enter the fuel tank, carrying an open flame is strictly prohibited. Reliable safety precautions must be in place, and there should be someone outside the tank for supervision.
7、All electrical devices on the vehicle must have good insulation, and the generation of sparks is strictly prohibited. Vehicle work lighting should be safe lamps with a voltage of less than 36V.
8、When the fuel tank sedimentation pit is frozen, do not use an open flame for thawing. Instead, use hot water, steam for melting, or move the vehicle to a warm place for thawing.
9、During maintenance and repairs under the vehicle, the internal combustion engine should be turned off, the handbrake should be engaged, and the wheels should be securely chocked.
10、After repairing the vehicle and needing a test drive, it should be driven by a qualified person. The vehicle should not carry passengers or cargo. If a road test is necessary, it should have a test license issued by the traffic management authority.
11、When parking on a slope, downhill parking should be in reverse gear, and uphill parking should be in first gear. Wheel chocks or triangular wedges should be used to secure the tires.
Daily Maintenance and Maintenance of Fuel Tank Trucks
1、The driving part that carries the fuel tank is commonly referred to as the vehicle chassis. Generally, drivers are more knowledgeable about this part. The issue is that after installing the fuel pump on the fuel tank truck, we connect it to the engine to take power through the transmission shaft and power take-off. When using these two devices, special attention is required, as improper operation can render the power take-off unit useless.
2、For the use and maintenance of the fuel pump, it should be strictly in accordance with the instructions provided in the maintenance manual that comes with the truck.
3、Similarly, for the use and maintenance of the refueling machine, follow the instructions in the provided manual. The truck should come with an instruction manual.
4、If fuel discharges slowly or doesn't discharge at all, check the safety valve and filter net. These components should be checked and cleaned regularly.
5、The fuel tank and pipeline system should be cleaned periodically. Check if all connections in the pipeline system are secure and the seals are reliable.
6、To ensure the cleanliness of the fuel tank, both the tank and the fuel delivery system should be cleaned periodically. Lubricate the inner and outer joints of the fuel delivery hose with lubricating oil for easy assembly and disassembly. After each use of the fuel hose, make sure to cover both ends with caps to keep the interior clean.
7、The fuel loading should not exceed the rated loading capacity (calculated according to the density of the fuel).
8、The medium passing through the ball valve should not be excessively dirty to protect the sealing ring and extend the lifespan of the ball valve. Ball valves should not be operated in a semi-open or semi-closed state for an extended period, as it may lead to seal ring deformation. During driving, all ball valve handles should be in the closed position.
9、The inlet filter net should be regularly removed and cleaned to prevent oil residue from clogging the filter and affecting flow.
10、Keep the breather valve clean so that it remains in working condition. The spring inside the valve should not be changed arbitrarily to prevent affecting the ventilation and pressure relief effect. When the breather valve becomes blocked, it poses a risk of tank deformation.
11、To prevent fire accidents in fuel trucks, it is not allowed to strike components on the vehicle with metal objects if the exhaust pipe or muffler is damaged, if there is a fuel leak in the pipeline, if the grounding electrode is damaged or broken, as this can generate sparks. Firefighting equipment should always be prepared on the truck.
12、If the sedimentation pit of the fuel tank freezes, do not use an open flame to thaw it. Use hot steam or place the truck in a warm room to thaw it.
13、Before starting work, insert the anti-static rod into damp soil, and ensure that the grounding strap is properly connected. Maintain good static electricity conduction during the operation.
14、Before using the vehicle, check the fire extinguisher device. Personnel operating the fuel tank truck should be familiar with the proper use of the fire extinguisher and perform checks and maintenance according to its instructions.
15、Before operating the fuel tank truck, check for oil leaks in the pipeline system, check if the grounding wire is disconnected, inspect the exhaust pipe for damage, and address any issues before starting work.
16、When measuring fuel, follow the relevant regulations. In winter, if there is water in the self-priming pump, it must be completely drained to prevent pump body freezing.
17、When entering the fuel tank for work, ensure good ventilation. A safety guard should be outside the tank if necessary. It is advisable to wash the tank body with soapy water before commencing work. Maintenance should be carried out as required.
Safety Knowledge for Fuel Tank Trucks
(1) Prevention of Person-to-Person Static Electricity: During loading and unloading operations, contact and friction between the human body and the working object (fuel tank truck) and working materials are inevitable. This can easily generate static electricity and result in static discharges. If this coincides with flammable and explosive oil vapors, an explosion accident may occur. Operators must wear anti-static work clothing and anti-static shoes to ensure that their bodies are grounded. Additionally, the shoes worn should be made of thin nylon socks or other conductive materials. It is strictly prohibited to attach insulating films to the soles of anti-static shoes, and regular inspections should be carried out.
(2) Importance of Grounding for Static Electricity: From the perspective of the fuel tank truck, the main areas where static electricity is generated are the pump, filter, and pipelines. The amount of static electricity generated in the fuel loading system of the fuel tank truck is much higher than in the ground pipeline. To address static electricity hazards, the following measures must be taken: ① Grounding should be connected before fueling, and its integrity and ground resistance should be regularly checked to ensure compliance with anti-static standards. ② The loading hose must extend to the bottom of the tank, and the distance between the hose opening and the tank bottom should be maintained at about 15 cm. The initial filling speed should be strictly controlled to be within 1 m/s until the discharge opening is submerged. Only then should the flow rate be gradually increased, but the maximum flow rate should not exceed 4.5 m/s to prevent electrostatic accidents caused by splashing. ③ After loading is completed, grounding should only be disconnected after stable fueling for 5 minutes, as the potential of the oil surface needs to be maintained for several minutes due to the flow of oil within the tank. ④ Vigilance should not be relaxed just because there is good grounding. Static electricity grounding can only dissipate the static electricity on connected "conductors" (such as metal, human body, conductive fluids, etc.), and it is powerless or difficult to remove static charges on isolated conductors and non-conductors (such as oil, rubber, resin, glass) in a short time. Therefore, operators should follow operating procedures strictly and be attentive to potential hazards that may arise at any time, while also understanding the emergency procedures and rescue measures for handling various unexpected events.
(3) Accidents Caused by "Switching Refueling" Should Be Taken Seriously: This type of accident mainly occurs when a tank that previously contained gasoline is used to refuel diesel. Gasoline has a lower flash point than diesel, and if diesel is poured into a tank containing gasoline vapors, the gasoline vapor pressure is reduced as it is absorbed by the incoming diesel. Air is then drawn into the tank. A flammable mixture is formed at some point between the liquid surface and the air inlet, and electrostatic discharge can trigger an explosion accident. Therefore, when there is a need for "switching refueling," the gasoline must be thoroughly removed from the tank, and the operation must be carried out strictly according to procedures.
(4) Use Equipment that Complies with Technical Specifications and Safety Requirements: Equipment such as self-control, remote control, measuring instruments, valves, and other devices in the fuel dispensing system must undergo regular inspection and calibration. Relevant management systems should be established, especially for the material of fuel dispensing equipment, which should not be taken lightly. Similarly, anti-static grounding devices should not be compromised. They must be installed rigorously in accordance with specifications and undergo regular checks. For systems that use clamps and magnetic couplings for grounding, they should not be haphazardly placed or attached to random parts of the fuel tank truck, including painted surfaces. This is detrimental to the effectiveness of anti-static grounding and represents a significant hazard. Many users are often tempted by low-cost options when purchasing equipment, not realizing that you get what you pay for. Substandard equipment can easily lead to accidents, and for fuel tank trucks, which transport dangerous goods, extra attention is necessary.
Fault Analysis
I. Engine Deceleration and Automatic Shutdown
When the engine running and the accelerator pedal is released or when the vehicle is moving, and the engine shuts down automatically, the root cause is that the engine's idle stability is poor when transitioning from non-idling to idling. Specific reasons may include a faulty throttle pedal, unsynchronized signals between the crankshaft position sensor and the camshaft position sensor, fuel pressure issues, incorrect control unit signals, and incorrect fuel injection timing, among others. Emphasis should be placed on examining the changes in values when transitioning from non-idling to idling.
II. Insufficient Engine Power or Poor Acceleration
The symptom of insufficient engine power is when the engine runs normally at no load but experiences slow acceleration, lack of power when going uphill, and insufficient power even when the accelerator pedal is fully depressed, causing the engine speed to remain constant without reaching the maximum speed. The symptom of poor engine acceleration is when depressing the accelerator pedal does not result in an immediate increase in engine speed and there is a delay or slight fluctuations during acceleration. The reasons for insufficient engine power and poor acceleration may include excessively high or low fuel system pressure, poor fuel injection, incorrect sensor signals, insufficient fuel injection, incorrect fuel injection timing, low cylinder compression pressure, and exhaust pipe blockages, among others.
III. Engine Cannot Start or Has Difficulty Starting
Starting faults in electronically controlled diesel engines are influenced by multiple factors. They typically manifest as failure to start (no initial combustion) or difficulty in starting. The following methods can be used to check and eliminate these issues:
Check for fault codes. If any fault codes are present, conduct inspections based on the code's content.
Check if the engine can rotate when starting.
(1)If the starter does not turn when starting, inspect the starting system for faults. First, check the battery charge status and the connection and contact of the battery terminals. If they are normal, check the starting circuit, fuses, and ignition switch.
If the starter turns but the engine does not, this indicates a fault in the engagement between the starter and the engine.
(2)If the engine rotates at a normal speed during starting but fails to start, check the fuel injection system and the intake system separately.
For electronically controlled fuel injection systems, no accelerator pedal needs to be pressed during starting. If fully depressing the accelerator pedal during starting or repeatedly pressing it in an attempt to increase fuel supply leads to a momentary increase in engine speed, resulting in increased fuel consumption, this suggests a malfunction with the throttle pedal.
(2)Visual inspection: Check the intake system for air leaks.
Fuel system inspection: Check the connection status of fuel lines, air intake issues, and fuel quality.
Wire harness inspection: Check for loose connections or loose plugs in the wiring harness.
Sensor inspection: Inspect whether sensors are malfunctioning, if wiring is loose or broken, and whether the crankshaft and camshaft have synchronized signals.
Check for injector control signals. If there are no control signals, inspect fuses, wiring, and the ECU. If there are control signals, inspect whether the fuel injectors spray normally.




